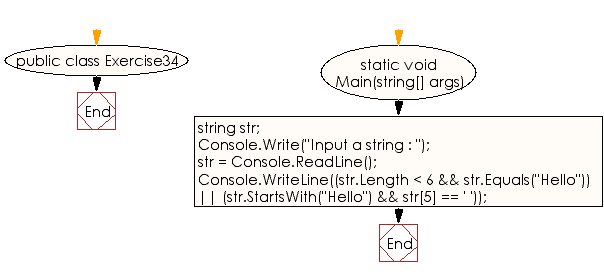
Ruby String Comparison Equal
For example a plus.
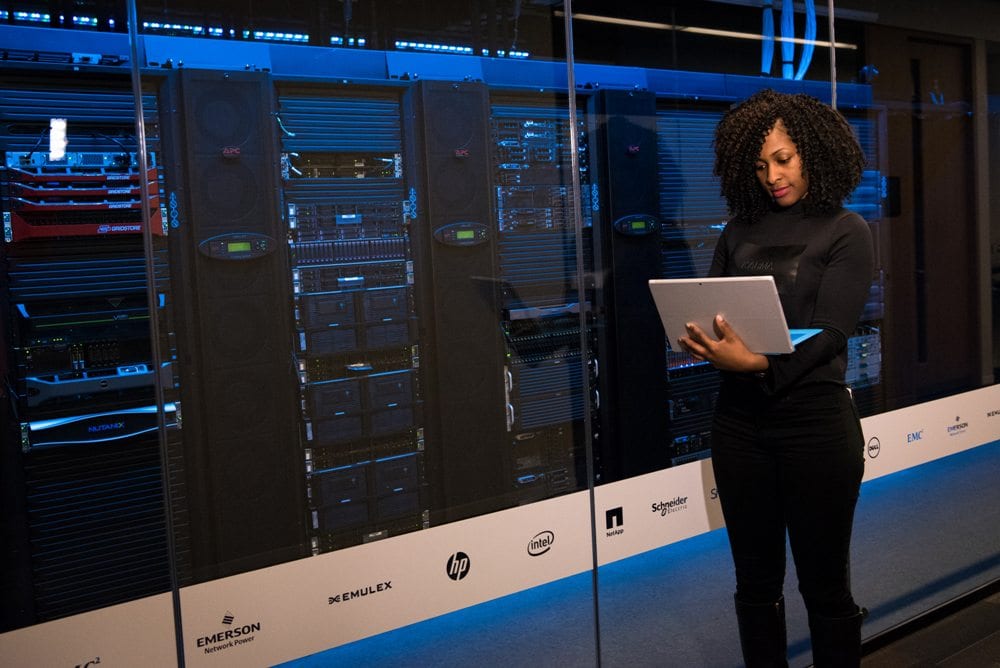
Ruby string comparison equal. Then ruby would use object s implementation of which defaults to testing for object identity instead of object contents. For each operator plus. Ruby supports a rich set of operators as you d expect from a modern language. For example 1 1 1 will return true because the numbers on both sides represent the same value.
Comparison operators take simple values numbers or strings as arguments and used to check for equality between two values. John fred false john eql. But what if string didn t implement. Equality is performed either using the or eql.
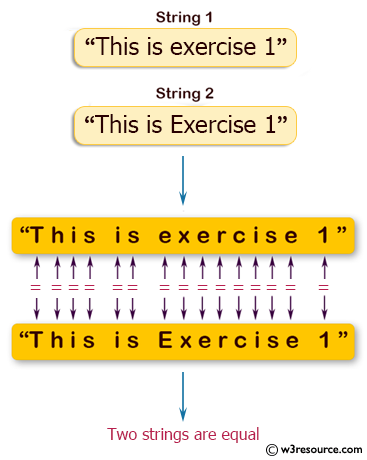
Many of ruby s built in classes such as string range and regexp provide their own implementations of the operator also known as case equality triple equals or threequals. B is interpreted as a plus b where the plus. Notice that we use two equal symbols to mean equality. If the strings are of different lengths and the strings are equal when compared up to the shortest length then the longer string is considered greater than the shorter one.
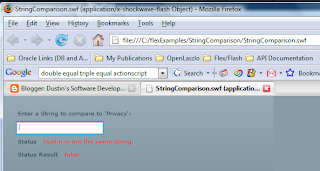
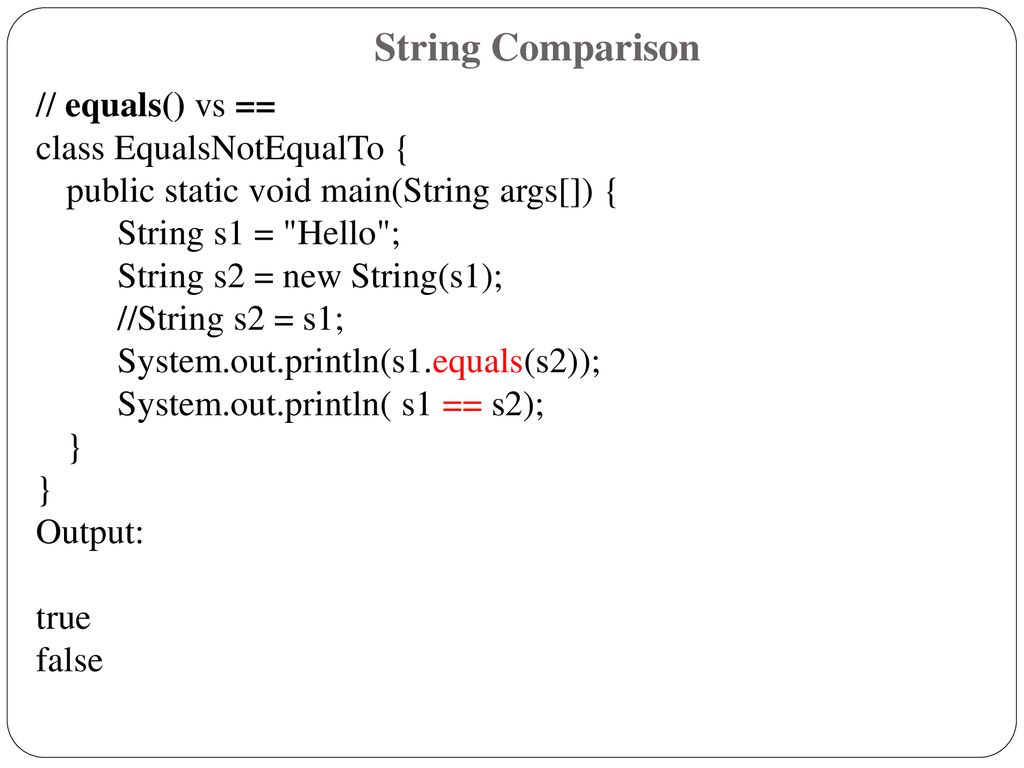
One equals sign in ruby means assignment make sure to use when you want to find out if two things are the same. The operator returns true if both objects can be considered the same. If you don t this right you won t get the expected results. Ruby string1 abc if abc string1 puts they are equal end but objects are frequently compared and tested for equality lsquo behind.
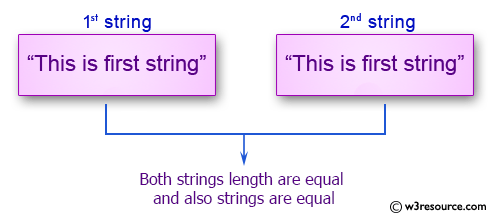
Method in the object referred to by variable a is called with b as its argument. Because it s implemented differently in each class it will behave differently depending on the type of object it was called on. This works because the string class implements a two equal signs method that knows how to compare strings. Comparison returns 1 0 1 or nil depending on whether string is less than equal to or greater than other string.
Nil is returned if the two values are incomparable. Object comparison is extremely important not only do we tend to often explicitly compare objects to each other e g. In order to compare things ruby has a bunch of comparison operators. Just like other object oriented languages ruby gives an object ways to find out if it is equal to greater or less than another object.
The expression a a also returns true because both strings have the same value. Object new object new false string new string. But when you want to check for the opposite not true false. Most operators are actually method calls.