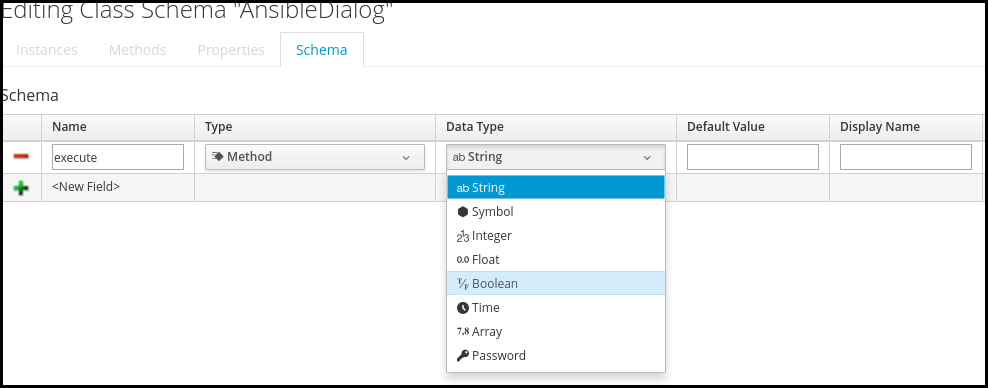
Ruby Instance Variable Default Value
New ada p person.
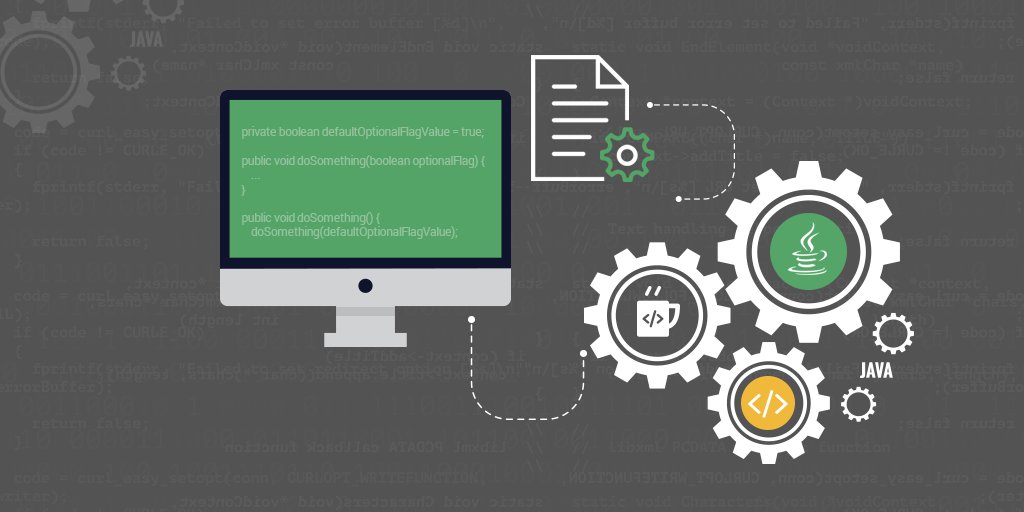
Ruby instance variable default value. It s also a falsy value meaning that it behaves like false when used in a conditional statement. I ve been toying with ruby for over a year but only in the last two months have i really started to code in. An undefined instance variable always returns nil. Well nil is a special ruby object used to represent an empty or default value.
There are advanced ways to access instance variables like instance variable get but you should avoid these. Ruby local variables are defined with and their. For instance in the above example you cannot simply call t value or t value to access the instance variable value this would break the rules of encapsulation this also applies to instances of child classes they cannot access instance variables belonging to the parent class even though they re technically. Class and instance variables in ruby.
I posted a bit more on the topic with example uses in the wild. Class variables are initialized with and will be defined inside the class. Uninitialized instance variables have the value nil and produce warnings with the w option. The first line creates a new instance of the class person passing the string ada and assign this new object to the variable person.
All instance variables are private by default. Every instance variable is dynamically. Instance variable have the value nil before initialization. Btw you can get a list of instance variables.
If you create and output an instance of our class person you ll see that ruby now prints out the instance variable too. The second line will then print it out. First let me preface this article with a fact. Instance variables begin with commat.
Instance variables don t have to be created in the initialize method but that s how you give them an initial value. Here is an example showing the usage of instance variables. There is only one nil object with an object id of 4 or 8 in 64 bit ruby this is part of why nil is special. The ruby instance variables do not need a declaration.
You normally cannot access instance variables from outside of an object. This implies a flexible object structure. Whenever ruby creates a new object it looks for a method named initialize and executes it. So one simple thing we can do is use an initialize method to put default values into all the instance variables so the inspect method will have something to say.
I m new to ruby however new is relative in that statement. The instance variables of an object can only be accessed by the instance methods of that object.